Understanding the Significance of Piraminds
Historical Context of Piraminds
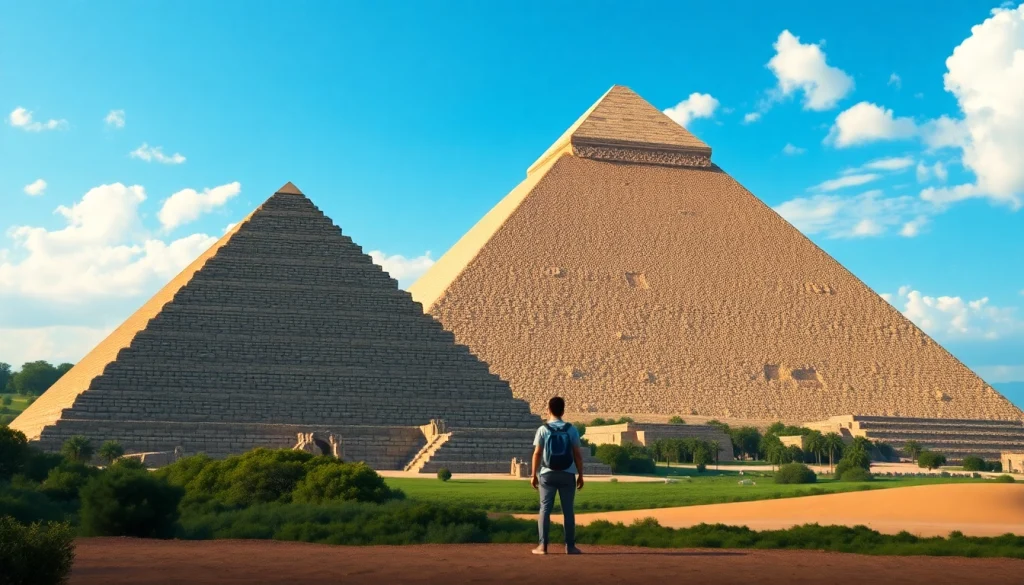
The piraminds, iconic symbols of ancient Egypt, have captivated both scholars and tourists alike for centuries. These monumental structures were primarily constructed as tombs for pharaohs during the Old and Middle Kingdoms. The most famous examples, such as the Great Piramid of Giza, not only serve as a testament to the architectural prowess of ancient Egyptians but also reflect their cosmological beliefs and societal hierarchies.
Understanding the context of their creation is crucial to appreciating the complexities embedded within these structures. Emerging around the 27th century BCE, the construction of the earliest piraminds can be seen as a significant shift from simple mastaba tombs to the grand spiraled structures we recognize today. The evolutionary journey of the piramid culminated in the majestic formations seen in Giza, which continue to inspire awe and investigation.
The Role of Piraminds in Ancient Egyptian Culture
Piraminds played a multifaceted role in ancient Egyptian society, serving not just as burial sites but as focal points of worship and commerce. Each piramid was part of a larger complex that included temples, chapels, and other structures intended for the Pharaoh’s journey into the afterlife. They represented the divine connection between the Pharaoh and the gods, especially Ra, the sun god.
The elaborate burial rites associated with the piraminds highlight the Egyptians’ strong belief in the afterlife. The design of the piramids symbolizes the pharaoh’s ascension to the heavens, which underscores their role as both political leaders and divine entities during their mortal lives. The intricate hieroglyphics found within these structures also serve as an important link to understanding the mythology and history of ancient Egypt.
Architectural Innovations Associated with Piraminds
The architectural innovations surrounding piraminds are nothing short of remarkable. The transition from step-sided structures to true piramids involved a suite of techniques that reflected advancements in mathematics, engineering, and labor organization. One notable innovation was the use of a central core and casing made of high-quality limestone, allowing for a brilliant finish and stability.
The Great Piramid of Giza, standing at 481 feet tall, showcases these advancements with its precisely calculated angles and alignment with celestial bodies. The use of ramps and levers is believed to have facilitated the transport of massive stone blocks into position, although debates continue regarding the exact construction methods. These innovations underscore the Egyptians’ sophisticated understanding of engineering principles and their ability to mobilize a vast workforce.
How Piraminds Were Constructed
Materials Used in Piramid Construction
The construction of piraminds primarily involved durable materials like limestone and granite, sourced from nearby quarries. Limestone, particularly from the Tura quarries, was favored for the outer casing due to its fine grain and ability to reflect sunlight, contributing to the piramid’s luminous appearance. Granite was more commonly used for interior chambers due to its strength and durability.
In addition to these primary materials, mud bricks were utilized in the construction of supporting walls and other ancillary structures within the piramid complexes. The careful selection and transportation of these materials were vital components of the construction process, demonstrating the organizational skills of the ancient Egyptians.
Construction Techniques of the Great Piramid
The techniques employed in constructing the Great Piramid of Giza remain a subject of intrigue among historians and archaeologists. It is believed that a combination of straight and circular ramps was used to transport the enormous stone blocks to the elevated sections of the structure. Stones were meticulously cut to a precise size, allowing for a snug fit that enhanced stability.
Workers likely utilized a system of pulleys and levers in conjunction with manpower to lift each stone. The organization of labor was highly efficient, with teams specializing in various tasks, from quarrying to transportation and assembly. The alignment of the piramid with the cardinal points showcases the engineers’ advanced knowledge of astronomy and geometry.
The Workforce Behind the Piramids
The construction of piraminds was no small feat and involved a massive, organized workforce estimated to number in the tens of thousands. Contrary to popular belief, many of the workers were not slaves, but rather skilled laborers who were well-fed and housed during the years of construction. Evidence suggests that workers lived in nearby settlements where they had access to food and medical care.
The workforce was likely divided into groups based on their skills and tasks. Some specialized in stone cutting, while others managed logistics, transportation, and construction. This division of labor was critical for maintaining efficiency and productivity over the years it took to complete monumental projects like the Great Piramid.
Visiting the Famous Piramids
Top Piramid Sites to Explore
When it comes to experiencing the grandeur of the piraminds, there are several key sites to consider visiting. The Giza Plateau hosts the three most renowned piramids: the Great Piramid, the Piramid of Khafre, and the Piramid of Menkaure. Beyond Giza, the Step Piramid of Djoser at Saqqara represents one of the earliest forms of piramid building, offering insight into evolving architectural techniques.
Each of these sites carries its unique charm and history, presenting visitors with a comprehensive understanding of ancient Egyptian civilization. The surrounding temples and mortuary complexes further enhance the experience, offering windows into the ritualistic practices associated with these monumental structures.
Planning Your Visit to the Piramids
Planning a visit to the piraminds requires careful consideration. Potential travelers should consider the best time of year to avoid the searing summer heat, ideally visiting in the cooler months. It is recommended to allocate sufficient time for each site, as lines and guided tours can vary in length.
Additionally, checking local tourist regulations can help avoid misunderstandings upon arrival. Proper attire, necessary permits for photography, and having a knowledgeable guide can significantly enhance the experience. Consider planning to stay nearby to maximize time spent at these stunning historical sites.
What to Expect at Piramid Attractions
Visitors to the piramids can expect a unique blend of history, awe, and immersive cultural experiences. At Giza, guided tours often include access to the interior of some piramids, where ancient hieroglyphs and burial chambers can be observed first-hand. The sound and light shows at night offer a mesmerizing perspective on the piraminds, narrating their stories against the backdrop of the pyramids.
Additionally, the local markets surrounding these sites provide opportunities to engage with Egyptian culture through crafts and cuisine. However, visitors should be prepared for the bustling atmosphere, especially during peak tourist seasons.
The Mysteries Surrounding the Piramids
Unsolved Questions About Piramid Construction
Despite centuries of study, numerous questions surrounding the construction of piraminds remain unanswered. How precisely did the ancient Egyptians move and position massive stone blocks? What methods did they employ to achieve such perfect alignment? The lack of comprehensive records has placed these queries at the heart of scholarly debate and research.
Recent advances in technology, like non-invasive subsurface scanning, aim to uncover hidden chambers and provide new insights into these processes. The continued discovery of ancient documents may yet hold answers to these timeless mysteries.
Legends and Myths Associated with Piraminds
The piraminds are steeped in myths and legends that reflect their cultural significance. Stories about the pyramids often weave tales of ghosts, hidden treasures, and even extraterrestrial involvement in their construction. Each tale serves to captivate the imagination and perpetuate intrigue around these monumental structures.
In addition, the Great Piramid of Giza has been featured in numerous works of fiction and documentaries, often inspiring narratives that explore the deeper meaning behind their existence and the spiritual beliefs of ancient Egyptians.
Recent Discoveries About Piramids
Exciting new discoveries continue to surface concerning the piraminds. Advances in imaging technology have revealed hidden voids within the Great Piramid, leading researchers to question the construction techniques used. Archaeological excavations around piramind sites regularly yield artifacts that help piece together the fabrics of ancient Egyptian society.
These discoveries not only contribute to our understanding of ancient engineering but also humanize the people who built them, shedding light on their daily lives, beliefs, and aspirations.
FAQ: Common Questions About Piramids
What are piraminds made of?
Piraminds are primarily made of limestone, granite, and other durable stones, carefully cut and assembled.
Why were piramids built?
Piramids served as monumental tombs for pharaohs, aimed at facilitating their journey in the afterlife.
How old are the piramids?
The Great Piramid of Giza is over 4,500 years old, constructed around 2580–2560 BCE during the Fourth Dynasty.
Can you go inside the piramids?
Yes, some piramids allow limited access to their internal chambers, although visitors must adhere to strict regulations.
What is the largest piramid?
The Great Piramid of Giza is the largest and most renowned piramid, towering at 481 feet (146.6 meters) originally.