Understanding the Basics of Transportation
What is Transportation?
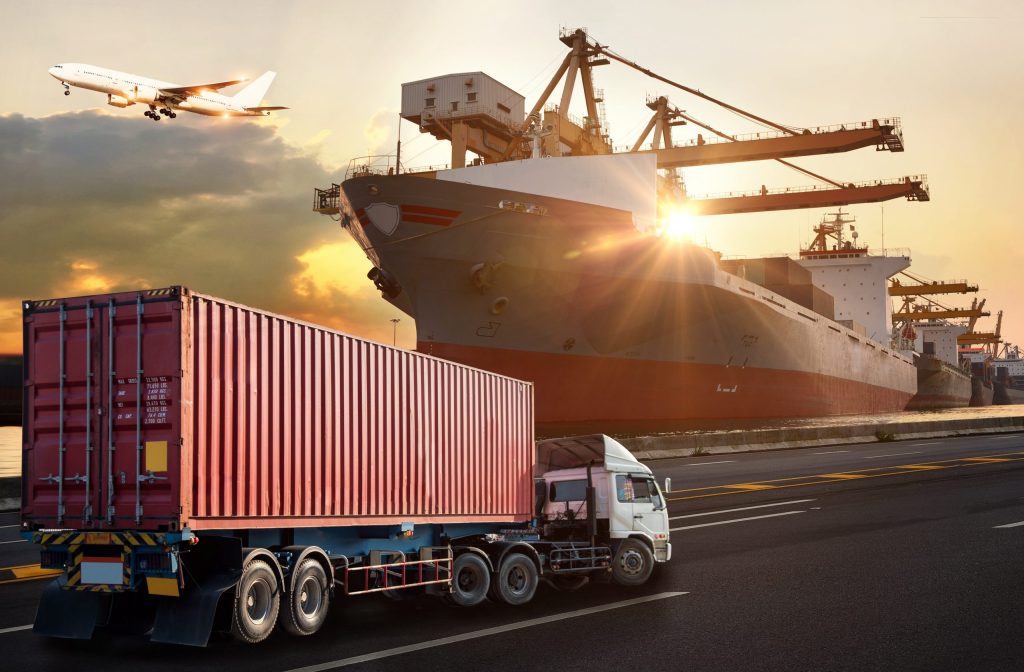
Transportation refers to the systematic movement of people, goods, and services from one place to another. It encompasses various modes of travel, including land, air, and water, and involves multiple means such as cars, buses, trains, airplanes, ships, and much more. The essence of transportation is deeply rooted in the evolution of human civilization, impacting economic growth, social interaction, and environmental development. For more information on the multifaceted world of transportation, we can explore both its historical context and modern implications.
History and Evolution of Transportation
The history of transportation can be traced back to prehistoric times when humans used their feet to traverse landscapes. As societies evolved, various means of transportation were developed. The invention of the wheel marked a significant turning point, leading to the creation of carts and chariots around 4000 BCE in Mesopotamia. Water transportation followed, with ancient civilizations using boats and ships for trade and exploration, as evidenced by the maritime activities of the Egyptians, Greeks, and Phoenicians.
In the 19th century, the Industrial Revolution brought about dramatic changes. The introduction of steam engines facilitated the development of railroads, which revolutionized long-distance travel and freight transport. This era saw the emergence of bicycles, cars, and the advent of commercial aviation in the 20th century, enabling rapid movement and connectivity globally.
Today, transportation continues to evolve, influenced by advances in technology, urbanization, and changing public needs. Innovations such as electric vehicles, autonomous transport, and the use of data analytics are reshaping the landscape, promising even faster and more efficient systems in the future.
Types of Transportation: An Overview
Transportation modes can be broadly classified into several categories:
- Land Transportation: This includes transportation via roads (cars, buses, bicycles) and rail systems (trains, subways). It is one of the most commonly used forms for both intracity and intercity travel.
- Water Transportation: Encompassing sea, river, and lake travel, this type includes cargo ships, fishing vessels, and cruise liners. Water transport is efficient for moving large quantities over long distances.
- Air Transportation: This involves the movement of passengers and goods via airplanes and helicopters. Air transport is the fastest method for long-distance travel and is increasingly becoming accessible for both freight and personal use.
- Pipeline Transportation: Used primarily for transporting liquids and gases, pipelines provide a reliable means of moving resources such as oil, water, and natural gas.
Modern Transportation Systems
Public vs. Private Transportation
Transportation systems today exist largely in two forms—public and private. Public transportation involves government or third-sector services that provide transportation to the public at large, such as buses, trains, subways, and ferries. This mode is typically more economical and environmentally friendly, reducing traffic congestion and the carbon footprint by minimizing the number of vehicles on the road.
Conversely, private transportation includes personal vehicles, taxis, and rideshare services. While often more convenient, they tend to contribute to exacerbating traffic and environmental concerns. Striking the right balance between public and private transportation is crucial for sustainable urban development.
The Role of Technology in Transportation
Technology has been a major driver of change in transportation systems. From the use of GPS systems that allow for real-time navigation to the widespread adoption of ride-sharing apps that redefine urban mobility, technological advancements have significantly enhanced connectivity and efficiency. Hyperloop systems and electric autonomous vehicles are at the forefront of modern transport innovations, promising to reshape our future mobility solutions.
Moreover, the analysis of big data has transformed how transportation authorities manage traffic flow, schedule public transit, and devise infrastructure improvements. Technology not only fosters greater efficiency but also improves safety through state-of-the-art communication systems that alert drivers and passengers to potential hazards.
Sustainable Transportation Solutions
As climate change continues to be a pressing issue, the transportation sector is increasingly focused on sustainability. Solutions such as electric vehicles, investment in public transit infrastructure, and the promotion of active transportation modes like cycling and walking are gaining traction.
Governments and organizations worldwide are implementing policies aimed at reducing emissions, including incentives for electric vehicle purchases and initiatives to increase public transit ridership. Innovative projects like bike-sharing programs and car-free city zones exemplify the shift toward a more sustainable future.
Challenges in the Transportation Sector
Infrastructure and Maintenance Issues
One of the major challenges facing transportation systems is inadequate infrastructure. Aging roads, bridges, and transit facilities require significant investment for maintenance and upgrades. Poor infrastructure can lead to inefficiencies, increased travel times, and, ultimately, greater vehicular emissions.
To address these challenges, urban planners and transport authorities need to prioritize infrastructure development, backed by funding from both public and private sectors. Regular assessments of infrastructure health, coupled with innovative construction materials and techniques, can extend the lifespan of transport systems.
Environmental Impact of Transportation
The transportation sector is one of the highest contributors to greenhouse gas emissions globally, accounting for approximately 14% of all emissions. The reliance on fossil fuels for transportation contributes significantly to air pollution and climate change.
Mitigating the environmental impact requires comprehensive strategies that encompass the transition to cleaner energy sources, promotion of public transit, and enhancement of non-motorized transport options such as biking and walking. Encouraging sustainable practices in logistics and freight transport is equally important for reducing environmental footprints.
Traffic Management and Safety Concerns
Traffic congestion remains a critical issue for urban areas, leading to wasted time, heightened stress for commuters, and increased fuel consumption. Effective traffic management systems that leverage technology can help alleviate these problems. Smart traffic signals, congestion pricing, and coordinated public transport services are some strategies employed to enhance flow and reduce bottlenecks.
Safety concerns in transportation are also paramount, with road accidents being a leading cause of injury and death worldwide. Implementing advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), stricter enforcement of traffic regulations, and public awareness campaigns are essential steps toward improving safety in transportation systems.
Best Practices for Effective Transportation
Optimizing Routes for Efficiency
To enhance operational efficiency in transportation, route optimization is critical. Utilizing advanced route planning software and algorithms can lead to reduced travel times and lower operational costs. Transportation firms can benefit from integrating real-time traffic data and predictive analytics, allowing them to anticipate delays and capitalize on favorable conditions.
Best practices include regularly reviewing and adjusting routes based on traffic patterns, ensuring flexibility in scheduling for higher efficiency, and encouraging drivers to adopt smoother driving behaviors that promote fuel efficiency.
Utilizing Public Transportation Effectively
Public transportation systems can significantly ease the burden of urban travel when utilized effectively. Authorities should focus on increasing the quality and frequency of services to enhance rider experience. Improvements in cleanliness, safety measures, and customer service can foster higher ridership.
Moreover, public awareness and outreach campaigns can educate citizens about available services, fare structures, and potential benefits, including cost savings and convenience. Integrating technology, such as mobile ticketing and GPS-enabled tracking apps, further enhances user-friendliness and accessibility.
Future Trends in Transportation Services
The future of transportation is set to be dominated by innovation and technology. Anticipated trends include the rise of electric and autonomous vehicles, which promise to decrease travel costs and increase safety. Shared mobility solutions like ride-sharing and car-sharing platforms are poised to reshape urban environments, reducing individual car ownership.
Furthermore, smart city initiatives increasingly involve transportation aspects, aiming to create cohesive and efficient urban mobility solutions through integrated transport networks that harness internet-of-things (IoT) technologies. As sustainability takes center stage, the implementation of green transport solutions will also grow.
Measuring Transportation Performance
Key Performance Indicators for Transportation
Measuring the effectiveness of transportation systems is critical in optimizing operations and ensuring user satisfaction. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for transportation may include metrics such as travel time reliability, ridership levels, cost per mile, and environmental impact assessments. Adjusting strategies based on these metrics can lead to significant improvements in service quality.
Analyzing User Experience in Transportation
User experience is paramount in determining the success of any transportation system. Gathering user feedback through surveys and focus groups can unveil areas for improvement and guide service enhancements. Key factors influencing user experience include punctuality, affordability, safety, and comfort of transport modes.
Utilizing user experience metrics helps create more effective transportation services that meet the needs and preferences of travelers, ultimately driving higher ridership and customer loyalty.
Case Studies: Successful Transportation Models
A successful model can be seen in cities like Copenhagen, which prioritizes cycling. The city’s extensive network of bike lanes, along with supportive policies and infrastructure, has positioned it as a leader in sustainable urban transportation. Additionally, cities such as Singapore and Tokyo have demonstrated excellence in public transit efficiency and user satisfaction through integrated transport systems that facilitate seamless transfers between different modes.
Analyzing these successful case studies provides valuable insights that can be replicated in other cities, fostering improved connectivity, environmental stewardship, and enhanced commuter experiences across the globe.